3D-printing the first rocket on Mars.
That’s the goal Tim Ellis and Jordan Noone set for themselves when they founded Los Angeles-based Relativity Space in 2015.
At the time they were working from a WeWork in Seattle, during the darkest winter in Seattle history, where Ellis was wrapping up a stint at Blue Origin. The two had met in college at USC in their jet propulsion lab. Noone had gone on to take a job at SpaceX and Ellis at Blue Origin, but the two remained in touch and had an idea for building rockets quickly and cheaply — with the vision that they wanted to eventually build these rockets on Mars.
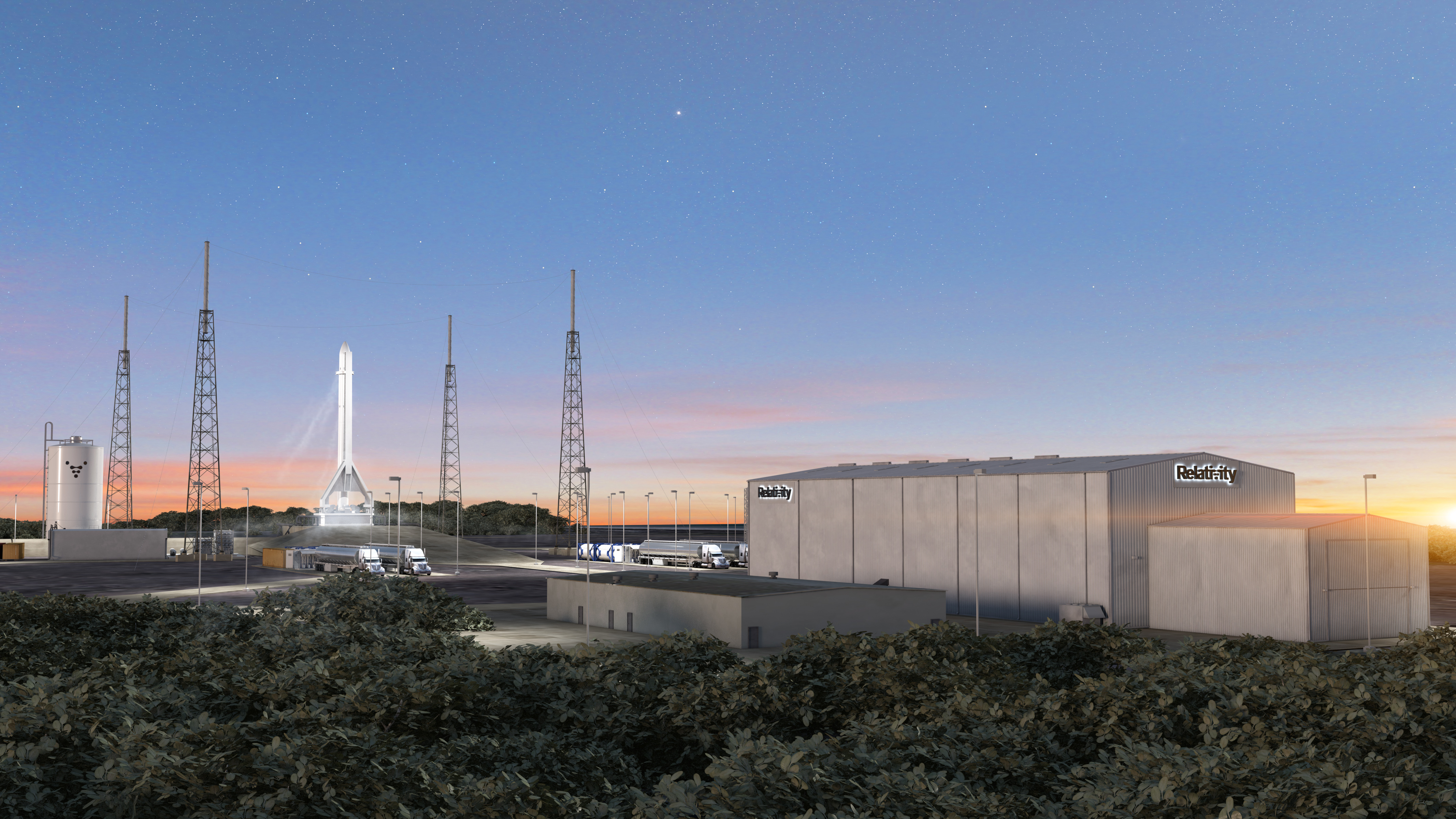
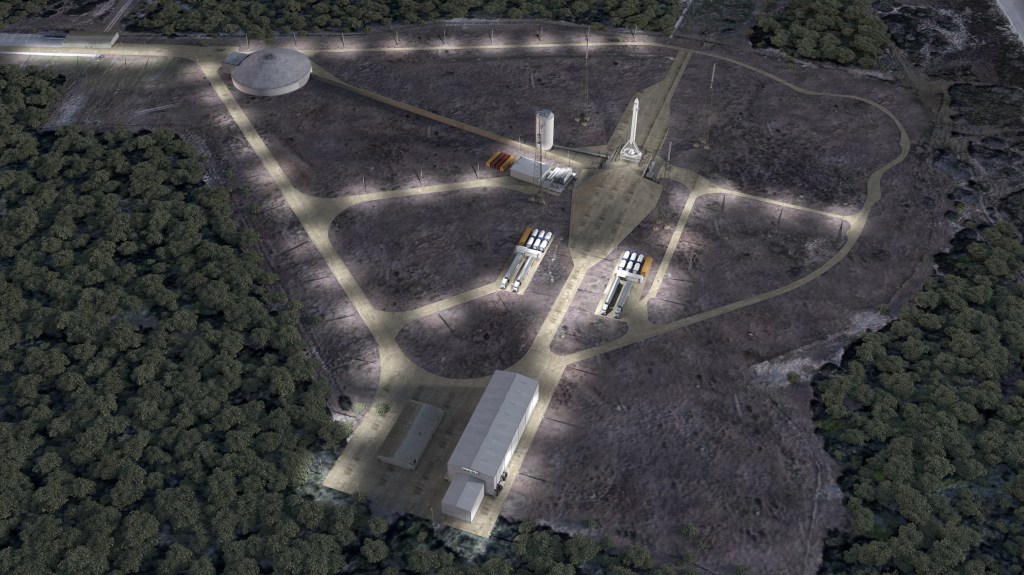
Now, more than $35 million dollars later, the company has been awarded a multi-year contract to build and operate its own rocket launch facilities at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
That contract, awarded by The 45th Space Wing of the Air Force, is the first direct agreement the U.S. Air Force has completed with a venture-backed orbital launch company that wasn’t also being subsidized by billionaire owner-operators.
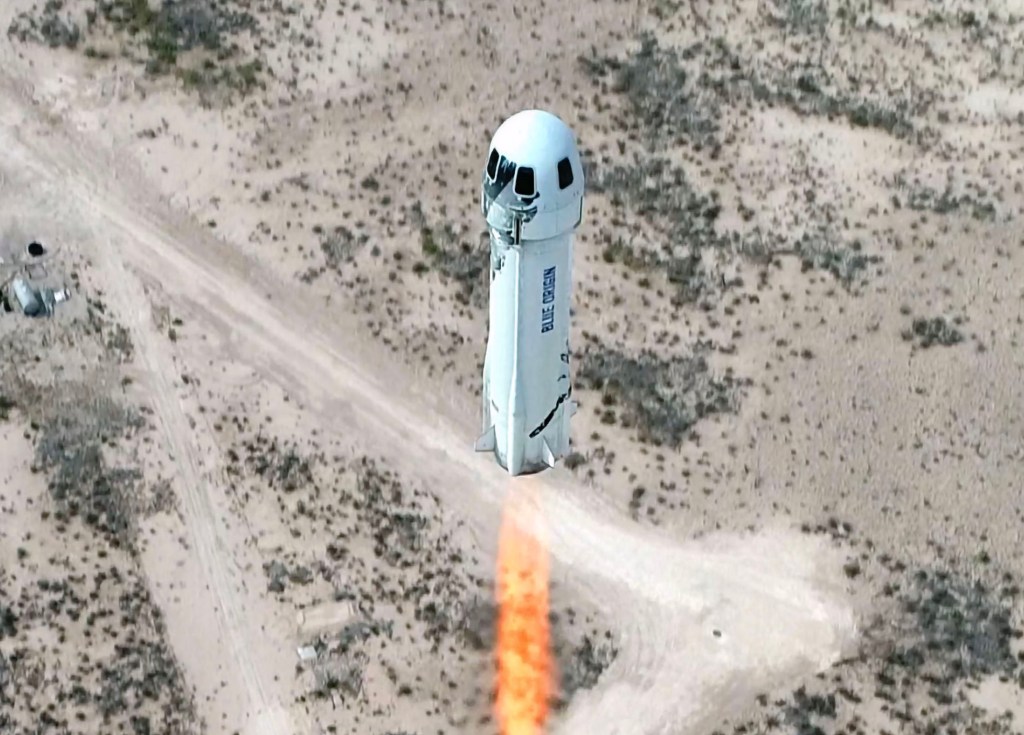
By comparison, Relativity’s neighbors at Cape Canaveral are Blue Origin (which Jeff Bezos has been financing by reportedly selling $1 billion in shares of Amazon stock since 2017); SpaceX (which has raised roughly $2.5 billion since its founding and initial capitalization by Elon Musk); and United Launch Alliance, the joint venture between the defense contracting giants Lockheed Martin Space Systems and Boeing Defense.
Like the other launch sites at Cape Canaveral, Launch Complex 16, where Relativity expects to be launching its first rockets by 2020, has a storied history in the U.S. space and missile defense program. It was used for Titan missile launches, the Apollo and Gemini programs and Pershing missile launches.

From the site, Relativity will be able to launch its first designed rocket, the Terran 1, which is the only fully 3D-printed rocket in the world.
That rocket can carry a maximum payload of 1,250 kilograms to a low earth orbit of 185 kilometers above the Earth. Its nominal payload is 900 kilograms of a Sun-synchronous orbit 500 kilometers out, and it has a 700 kilogram high-altitude payload capacity to 1,200 kilometers in Sun-synchronous orbit. Relativity prices its dedicated missions at $10 million, and $11,000 per kilogram to achieve Sun-synchronous orbit.
If the company’s two founders are right, then all of this launch work Relativity is doing is just a prelude to what the company considers to be its real mission — the advancement of manufacturing rockets quickly and at scale as a test run for building out manufacturing capacity on Mars.
“Rockets are the business model now,” Ellis told me last year at the company’s offices at the time, a few hundred feet from SpaceX. “That’s why we created the printing tech. Rockets are the largest, lightest-weight, highest-cost item that you can make.”
It’s also a way for the company to prove out its technology. “It benefits the long-term mission,” Ellis continued. “Our vision is to create the intelligent automated factory on Mars… We want to help them to iterate and scale the society there.”
3D-printed rocket maker Relativity raises $35M to simplify satellite launches
Ellis and Noone make some pretty remarkable claims about the proprietary 3D printer they’ve built and housed in their Inglewood offices. Called “Stargate,” the printer is the largest of its kind in the world and aims to go from raw materials to a flight-ready vehicle in just 60 days. The company claims that the speed with which it can manufacture new rockets should pare down launch timelines by somewhere between two and four years.
Another factor accelerating Relativity’s race to market is a long-term contract the company signed last year with NASA for access to testing facilities at the agency’s Stennis Space Center on the Mississippi-Louisiana border. It’s there, deep in the Mississippi delta swampland, that Relativity plans to develop and quality control as many as 36 complete rockets per year on its 25-acre space.
All of this activity helps the company in another segment of its business: licensing and selling the manufacturing technology it has developed.
“The 3D factory and automation is the other product, but really that’s a change in emphasis,” says Ellis. “It’s always been the case that we’re developing our own metal 3D printing technology. Not only can we make rockets. If the long-term mission is 3D printing on Mars, we should think of the factory as its own product tool.”
Not everyone agrees. At least one investor I talked to said that in many cases, the cost of 3D printing certain basic parts outweighs the benefits that printing provides.
Still, Relativity is undaunted.
But first, the company — and its competitors at Blue Origin, SpaceX, United Launch Alliance and the hundreds of other companies working on launching rockets into space again — need to get there. For Relativity, the Canaveral deal is one giant step for the company, and one great leap toward its ultimate goal.
“This is a giant step toward being a launch company,” says Ellis. “And it’s aligned with the long-term vision of one day printing on Mars.”































Comment