Leonard Kleinrock
When my team of graduate students and I sent the first message over the internet on a warm Los Angeles evening in October, 1969, little did we suspect that we were at the start of a worldwide revolution. After we typed the first two letters from our computer room at UCLA, namely, “Lo” for “Login,” the network crashed.
Hence, the first internet message was “Lo” as in “Lo and behold” – inadvertently, we had delivered a message that was succinct, powerful, and prophetic.
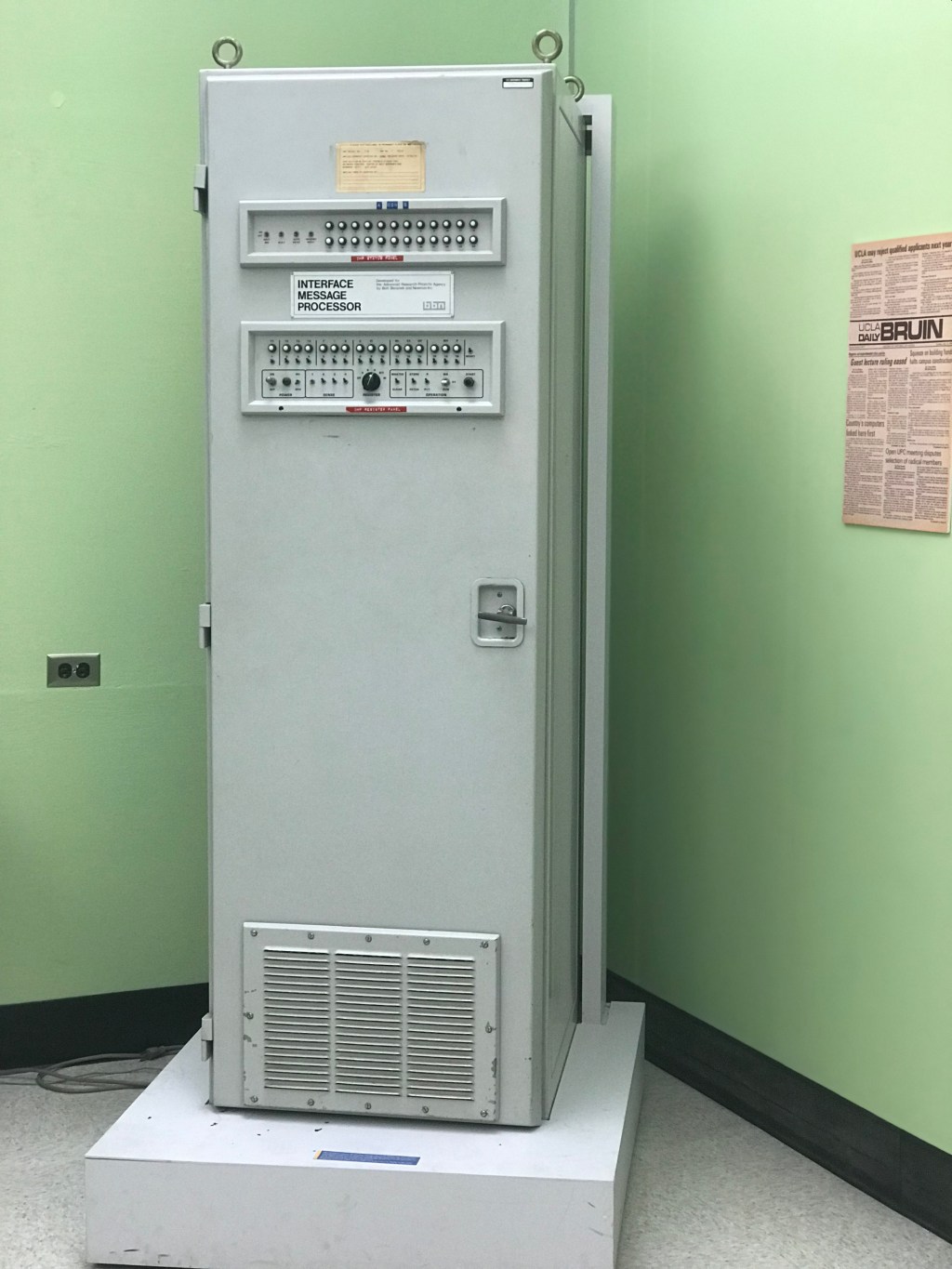
The ARPANET, as it was called back then, was designed by government, industry and academia so scientists and academics could access each other’s computing resources and trade large research files, saving time, money and travel costs. ARPA, the Advanced Research Projects Agency, (now called “DARPA”) awarded a contract to scientists at the private firm Bolt Beranek and Newman to implement a router, or Interface Message Processor; UCLA was chosen to be the first node in this fledgling network.
By December, 1969, there were only four nodes – UCLA, Stanford Research Institute, the University of California-Santa Barbara and the University of Utah. The network grew exponentially from its earliest days, with the number of connected host computers reaching 100 by 1977, 100,000 by 1989, a million by the early 1990’s, and a billion by 2012; it now serves more than half the planet’s population.
Along the way, we found ourselves constantly surprised by unanticipated applications that suddenly appeared and gained huge adoption across the Internet; this was the case with email, the World Wide Web, peer-to-peer file sharing, user generated content, Napster, YouTube, Instagram, social networking, etc.
It sounds utopian, but in those early days, we enjoyed a wonderful culture of openness, collaboration, sharing, trust and ethics. That’s how the Internet was conceived and nurtured. I knew everyone on the ARPANET in those early days, and we were all well-behaved. In fact, that adherence to “netiquette” persisted for the first two decades of the Internet.
Today, almost no one would say that the internet was unequivocally wonderful, open, collaborative, trustworthy or ethical. How did a medium created for sharing data and information turn into such a mixed blessing of questionable information? How did we go from collaboration to competition, from consensus to dissention, from a reliable digital resource to an amplifier of questionable information?

The decline began in the early 1990s when spam first appeared at the same time there was an intensifying drive to monetize the Internet as it reached deeply into the world of the consumer. This enabled many aspects of the dark side to emerge (fraud, invasion of privacy, fake news, denial of service, etc.).
It also changed the nature of internet technical progress and innovations as risk aversion began to stifle the earlier culture of “moon shots”. We are currently still suffering from those shifts. The internet was designed to promote decentralized information, democracy and consensus based upon shared values and factual information. In this it has disappointed to fully achieve the aspirations of its founding fathers.
As the private sector gained more influence, their policies and goals began to dominate the nature of the Internet. Commercial policies gained influence, companies could charge for domain registration, and credit card encryption opened the door for e-commerce. Private firms like AOL, CompuServe and Earthlink would soon charge monthly fees for access, turning the service from a public good into a private enterprise.
This monetization of the internet has changed it flavor. On the one hand, it has led to valuable services of great value. Here one can list pervasive search engines, access to extensive information repositories, consumer aids, entertainment, education, connectivity among humans, etc. On the other hand, it has led to excess and control in a number of domains.
Among these one can identify restricted access by corporations and governments, limited progress in technology deployment when the economic incentives are not aligned with (possibly short term) corporate interests, excessive use of social media for many forms of influence, etc.
If we ask what we could have done to mitigate some of these problems, one can easily name two. First, we should have provided strong file authentication – the ability to guarantee that the file that I receive is an unaltered copy of the file I requested. Second, we should have provided strong user authentication – the ability for a user to prove that he/she is whom they claim to be.
Had we done so, we should have turned off these capabilities in the early days (when false files were not being dispatched and when users were not falsifying their identities). However, as the dark side began to emerge, we could have then gradually turned on these protections to counteract the abuses at a level to match the extent of the abuse. Since we did not provide an easy way to provide these capabilities from the start, we suffer from the fact that it is problematic to do so for today’s vast legacy system we call the Internet.

Having come these 50 years since its birth, how is the Internet likely to evolve over the next 50? What will it look like?
That’s a foggy crystal ball. But we can foresee that it is fast on its way to becoming “invisible” (as I predicted 50 years ago) in the sense that it will and should disappear into the infrastructure.
It should be as simple and convenient to use as is electricity; electricity is straightforwardly available via a trivially simple interface by plugging it into the wall; you don’t know or care how it gets there or where it comes from, but it delivers its services on demand.
Sadly, the internet is far more complicated to access than that. When I walk into a room, the room should know I’m there and it should provide to me the services and applications that match my profile, privileges and preferences. I should be able to interact with the system using the usual human communication methods of speech, gestures, haptics, etc.
We are rapidly moving into such a future as the Internet of Things pervades our environmental infrastructure with logic, memory, processors, cameras, microphones, speakers, displays, holograms, sensors. Such an invisible infrastructure coupled with intelligent software agents imbedded in the internet will seamlessly deliver such services. In a word, the internet will essentially be a pervasive global nervous system.
That is what I judge will be the likely essence of the future infrastructure. However, as I said above, the applications and services are extremely hard to predict as they come out of the blue as sudden, unanticipated, explosive surprises! Indeed, we have created a global system for frequently shocking us with surprises – what an interesting world that could be!






























Comment